Agricultural Robots Simulation Environment
A simulation environment for under-canopy agricultural field robots
This project is related to our work Learning to Turn: Diffusion Imitation for Robust Row Turning in Under-Canopy Robots, aiming to explore agricultural field robot policy learning with Sim2Real. Thus, an important piece of this work is to build a realistic simulation environment to collect simulated data, which is challenging due to the unstructureness of field environments.
Methods
IsaacGym
The initial idea was to use the recently developed simulator IsaacGym to build a customized simulation environment, as it has been widely used for robot policy learning. Moreover, we wanted to leverage its ability of runnning environments in parallel to accelerate data collection pipeline.
In IsaacGym, we implemented the following features:
- Converted prepared models of crop variants (corn, tabacco, and soybean) and the field robot in SDF form to URDF form
- Developed a pipeline to generate 20 random croprow grid layouts for simulation at a time from a config file and load the assets into the simulator
- Configured RGB-D cameras to capture depth and image data
- Leveraged GPU acceleration to maintain a image rendering rate of 20 FPS across parallel environments
However, experiments showed that the visual quality of rendered images from IsaacGym was not ideal for Sim2Real usage. Specifically, the lack of support for materials over object surfaces and poor rasterization effects limit the quality of RGB images, while the quality of depth images was decent.
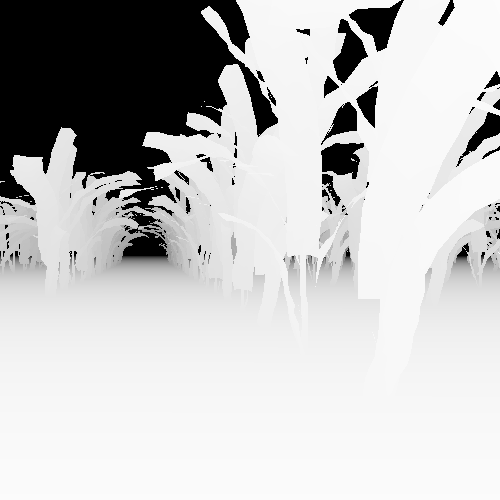
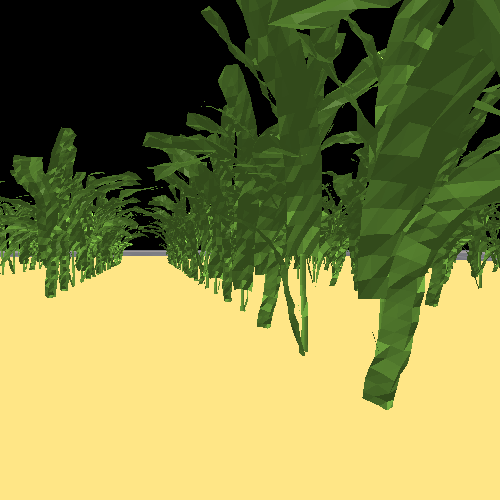

The repo for the IsaacGym environment can be found at here.
Gazebo
We chose Gazebo to be the solution to build our environments on. Although it provided rendered images with higher quality than IsaacGym, it limited the efficiency to collect massive amount of data without parallel environments. As a result, we developed an automatic data collection pipeline as well as some other features to migrate our design from IsaacGym:
- Refined the pipeline to generate random croprow layouts by adding customizations for crop orientations, heights, distance between crops …
- Configured and added three RGB-D cameras to the robot agent in URDF format using camera sensor plugins provided by Gazebo
- Commanded the robot agent to follow defined trajectories using a MPC controller with ROS
- Automated the data collection pipeline by using the
subprocesspackage in Python to terminate and restart the simulator and running Gazebo in headless mode - Integrated the function to use a PS4 controller to control the robot agent with the
teleop_twist_joypackage in ROS
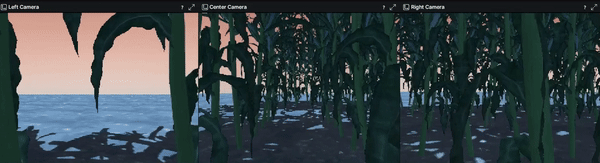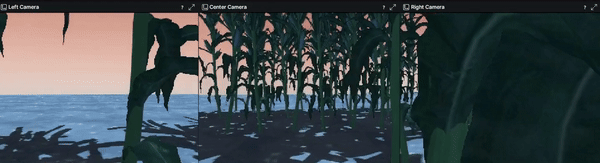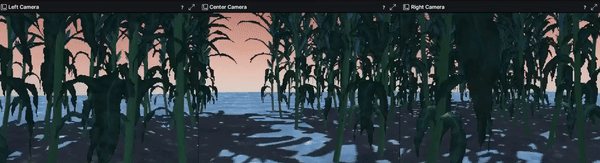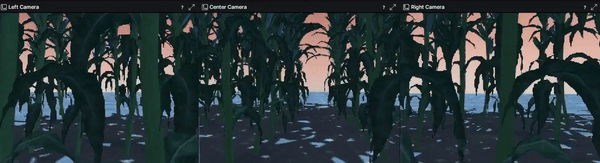
The repo for the Gazebo environment can be found at here.
Data Collection
Row-turning demonstration data can be collected either by commanding the robot to follow pre-defined trajectories or human teleoperation. In either way, data was recorded using ROS bags and extracted by ROS topic names. The following data was collected and synchronized:
- RGB images
- Depth images
- Goal position of each demonstration
- Trajectory of each demonstration (2D waypoints)
- Linear and angular velocities at each waypoint
The data was then further processed using the Zarr package. .zarr format files are similar to dictionaries with numpy arrays, but it can provide faster access to data during runtime by transferring them to RAM from disk space. In addition, data can be further compressed to save storage space. This will guarantee a significant speedup for model training time when loading data in .zarr format.
Skills Used
- Robotics Simulation: Gazebo, IsaacGym
- Robotics: ROS, MPC Controller, PID Controller, Differential drive dynamics
- Computer Vision and Graphics: Camera models, Image rendering and processing, rasterization
- Programming: Python, C++, CUDA
Acknowledgement
Special thanks to Dr. Arun N. Sivakumar and Jose Cuaran for helping me through this project. Some assets used in simulation are credit to the DASLAB at UIUC.